2024 Engagement and Retention Report
What is your employees’ emotional salary?
This resource is brought to you by:
Topics Covered:
Employee engagement
Retention is tougher than ever. 41% of employees plan to job hunt in 2024, and another 24% are on the fence — meaning two-thirds of your workforce could be at risk. Do you have a strategy in place to keep your top talent engaged?
The Engagement and Retention Report 2024 from Achievers Workforce Institute (AWI) reveals the real drivers of turnover — and how HR leaders can stop it. Yes, money matters, but it’s not the whole story.
So, how can you create a workplace where employee engagement takes center stage? It starts with understanding what truly drives their decisions and addressing those needs head-on.
What’s impacting employee retention in 2024?
Think compensation is the top reason employees are leaving? Think again.
Employees aren’t just chasing paychecks — they’re looking for opportunities to grow, feel appreciated, and work in a culture that supports them. If you focus only on salaries, you risk losing your best people to companies that offer more than just a paycheck.
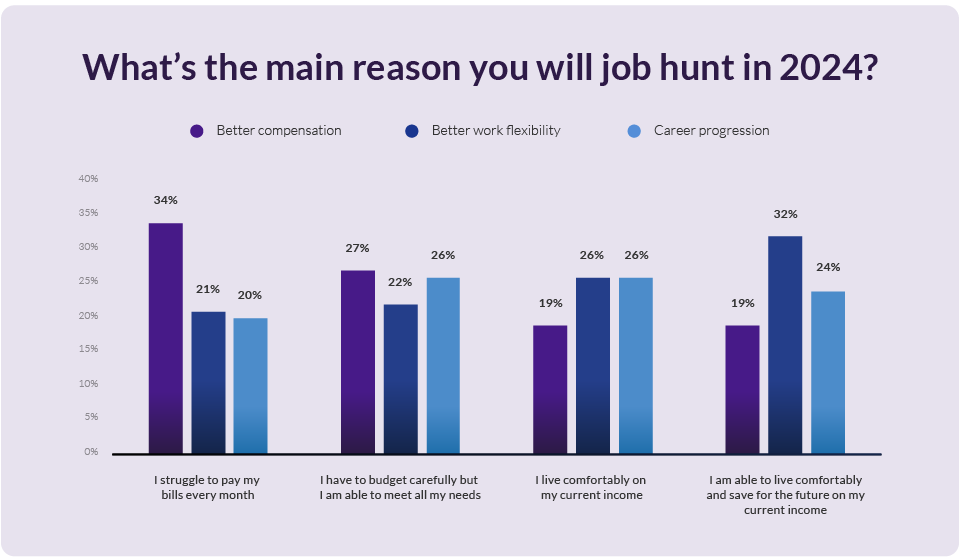
How HR leaders can drive employee engagement and retention
The solution? Emotional salary — the non-monetary factors that drive employee engagement and retention. By investing in career development, recognition, and work-life balance, companies can create a loyal, engaged workforce that feels valued and committed.
AWI has uncovered five powerful ways to boost emotional salary:
- Align culture with values
- Celebrate success with frequent recognition
- Foster strong work relationships
- Provide consistent, actionable feedback
- Offer clear paths for career progression
Don’t wait until employees hand in their notice. Get ahead of the curve with research-backed strategies to keep employee engagement and loyalty at the forefront of your organization.
Download the Engagement and Retention Report 2024 now to discover actionable insights to help you retain your top talent now and in the future or view our other annual employee engagement and retention reports.

Join our mailing list
Stay up to date with the latest in workforce science from Achievers Workforce Institute.